Ecology presentation
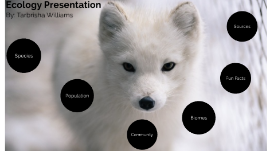
Transcript: By: Tarbrisha Williams Ecology Presentation The animal that I chose was a Arctic Fox Arctic foxes are native to the Arctic Regions of the Northern Hemisphere Arctic foxes are predators, and some examples of Prey for Adult foxes are: Polar Bears, other wolf packs, humans, birds, and snowy owls, which makes them Carnivores. Since Arctic foxes have to go out and get their food, they are considered to be Consumers. Species ~ Species Subtopic Arctic foxes sometimes survive in packs, just like any other fox species. They mostly hunt together, and sometimes encounter rival packs, which will sometimes result in the packs fighting each other. Arctic Foxes use certain sounds to communicate with each other, and they sometimes bury into the snow for protection. They also sometimes dig holes to store food. (For families) The Father wolf protects the den and also goes out and get food to support the familiy. Competition arises between the cubs, especially when food is Scarce. They will also fight each other to survive before leaving their families. Population Population Arctic foxes aren't the only animals that live in the Arctic regions. There are numerous different populations that live in a Tundra, mostly including the plants and animals. Community Community Arctic Foxes are found in the Arctic Reigons of the Northern Hemisphere, so they are found in the Tundra Biome. Some Biotic factors that are in a Tundra are: Fungi, Mosses, Shurbs, Insects, Fish, Birds, and Mammals. Some Abiotic factors in a Tundra are: Strong winds, rainfall, short summer days, and long, cold winters. Other species that live in the Arctic regions, along with the arctic foxes are: Arctic Hares, polar bears, Caribou, Snowy owls and many more. Biomes Biomes Fun Facts Fun Facts Arctic foxes are covered in thick white fur during the winter and have a greyish brownish fur in the summer Arctic foxes are small animals that can reach 26 inches in length and weigh 6.5 to 17 pounds. Arctic foxes have excellent senses such as hearing and smell, that can help find prey. Arctic foxes can survive for 3-6 years in the wild on their own Are monogamous animals (one couple mate for a lifetime) then they gather in March or April for mating season. Main predators for Arctic foxes (besides humans) are Red Foxes and Polar bears https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/arctic_fox.htm https://www.tutorvista.com/biology/abiotic-factors-of-the-tundra http://www.alaskakids.org/index.cfm/cool%20critters/featured%20critters/medium%20mammals/2613 https://beyondpenguins.ehe.osu.edu/issue/tundra-life-in-the-polar-extremes/life-in-the-tundra https://sciencing.com/biotic-abiotic-factors-in-the-tundra-12083312.html http://www.softschools.com/facts/animals/arctic_fox_facts/618/ My Sources Sources